South Korea’s electronics industry foreign investment surges to US$3 billion
tech
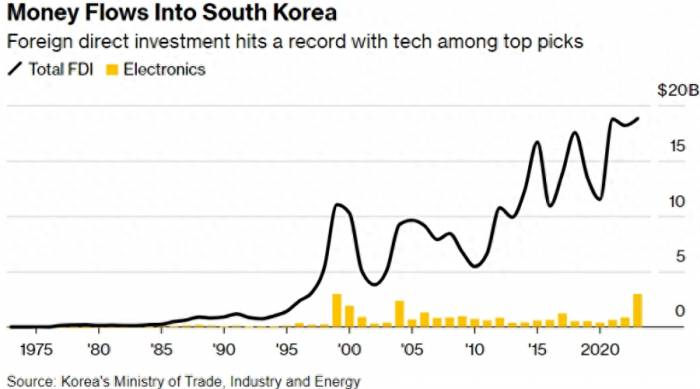
South Korea attracted a record high in foreign direct investment in 2023, indicating that global investors remain confident in the long-term prospects of the country's technology sector.
According to data from the Korean Ministry of Trade on January 4th, the funds inflow to South Korea in 2023 was approximately $18.8 billion, a year-on-year increase of 3.4%, with the electronics industry accounting for $3 billion. In contrast, foreign investment in the electronics sector was around $853 million in 2022.
Semiconductors and rechargeable batteries are the two main pillars of South Korea's electronics industry.
Despite the still sluggish global consumer demand for some technology products, including computers, semiconductors experienced a strong rebound at the end of 2023, with South Korean semiconductor shipments in December 2023 increasing by 21.8% compared to the same period in 2022. After achieving double-digit growth in November, exports of rechargeable batteries for electric vehicles declined by 1% in December on a month-over-month basis.
Advertisement
South Korea is home to the world's two largest memory chip manufacturers, Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix. Following a surge in demand for memory chips during the pandemic, the South Korean government is leading a plan to create a semiconductor cluster in the southern part of the capital.
In the field of rechargeable batteries, data from local research institution SNE Research shows that, as of October 2023, LG Energy Solution and two other South Korean companies held about 23.4% of the global electric vehicle battery market.
The data also indicates that South Korea's foreign direct investment commitments for 2023 reached a record $32.7 billion, a year-on-year increase of 7.5%, suggesting that funding from overseas may continue to grow.
SK Hynix's market value in South Korea has risen to the second position.South Korean chipmaking giant SK Hynix ranked second in market value on the South Korean stock exchange by the end of 2023, as part of a semiconductor stock recovery amid a slowdown in the growth of the country's battery manufacturers.
The South Korean Composite Stock Price Index rose by 18.7% in 2023, with six out of the top 10 companies by market value seeing their stock prices increase. In 2022, all top 10 companies, except for the newly listed LG Energy Solution, experienced declines due to a chip downturn and rising interest rates.
The undisputed leader is Samsung Electronics, whose market value increased by 42% in 2023 to 468 trillion won ($357 billion), as people anticipated a recovery from the chip downturn.
SK Hynix, with its advanced dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips selling well, saw its market value surge by 89% to 103 trillion won, while LG Energy Solution, the battery manufacturer ranked third on the list, fell by 2% to 100 trillion won.
Among the top 10 companies, SK Hynix's 89% increase was the most significant. Steelmaker POSCO Holdings' stock price rose by 81%, the second-largest increase, due to its main factory fully recovering from typhoon damage and expectations of increased profits from battery materials.
Hyundai Motor and its affiliate Kia saw their rankings rise, boosted by strong sales of high-end models in Europe and the United States, as well as expectations of record operating profits for the fiscal year ending in December. Hyundai Motor's market value increased by 33% to 43 trillion won, while Kia Motors' market value jumped by 67% to 40 trillion won.
Battery-related companies fared poorly, with the rankings of LG Chem, the parent company of LG Energy Solution, and major battery producer Samsung SDI also declining.
The growth in electric vehicle sales did not meet expectations, and the industry faces the risk of oversupply due to substantial capital investments. Uncertainty in the battery supply chain due to Sino-American tensions is also a contributing factor.
Online-focused technology companies also experienced a down year. With market saturation in South Korea and tighter platform regulations in Seoul, Kakao's growth rate was only 2%, dropping from the 10th position at the end of 2022 to the 14th. At the end of 2021, the company was as high as fifth in the rankings.
Naver remains in the eighth position due to expectations for its cloud business and the global expansion of its online comic platform.Coupang, a major online retailer listed on the New York Stock Exchange with a market capitalization of $28.9 billion, will lead Naver as the eighth-ranked company on the South Korean exchange. The company is expected to achieve profitability for the first time in 2023, with its stock price increasing by 10% year-over-year.
South Korea's chip production and shipment volumes are showing a double rebound, with the recovery momentum in the tech industry becoming increasingly evident.
South Korea plays a significant role in the global semiconductor supply chain and is often regarded as the "canary in the coal mine" for the global tech industry. Its chip production and shipment volumes are one of the closely watched indicators. Data released by the South Korean Bureau of Statistics has further strengthened market confidence in the recovery of the semiconductor industry, which is an extremely positive signal for the industry and the global tech sector.
The data shows that in November, South Korea's chip production increased by 42% year-over-year, marking the largest increase since early 2017; shipments surged by 80%, reaching the fastest growth rate since the end of 2002. Concurrently, inventory grew by 36%, the smallest increase since February, highlighting the strong market demand.
These figures indicate that South Korea's semiconductor industry is gradually recovering from a downturn that has lasted for over a year, which has also filled more chip manufacturers with confidence in the future market development.
Due to South Korea's heavy reliance on the semiconductor industry, the sluggish market in the past period has dragged down the overall growth of the South Korean economy. According to the Bank of Korea, due to rising interest rates, a slowdown in the overall economic development momentum in Asia, and the continuous emergence of geopolitical risks, South Korea's economy is expected to grow by only 1.4% this year, lagging behind the 2.6% growth in 2022.
However, the recovery of the chip industry is expected to boost South Korea's economy next year. The Bank of Korea forecasts that semiconductor exports will strengthen further after resuming growth in October this year, with the price of memory chips rebounding and the demand for chips increasing due to information technologies such as artificial intelligence, helping South Korea's GDP to achieve a 2.2% growth next year.
The South Korean Ministry of Finance also stated in a release that external demand for high-performance semiconductors has helped the chip and machinery industries. Assistant Economist Shannon Nicoll from Moody's Analytics pointed out that the expected global demand growth for South Korean goods will alleviate the adverse effects of local high inflation and high interest rates, and industrial production is also expected to rebound further.